Performance optimisation of the optical clock “SOC2”, installation and operation at Wettzell for geodesy and fundamental physics studies (P3)
P3 focuses on the installation and operation of the transportable optical clock “SOC2”. It will be the provider of accurate time signals to be sent from Geodetic Observatory Wettzell (GOW) to Potsdam via the ground-space links of the ACES mission. Alternatively, it can serve as the local clock at GOW with respect to which time signals arriving from ACES are measured.
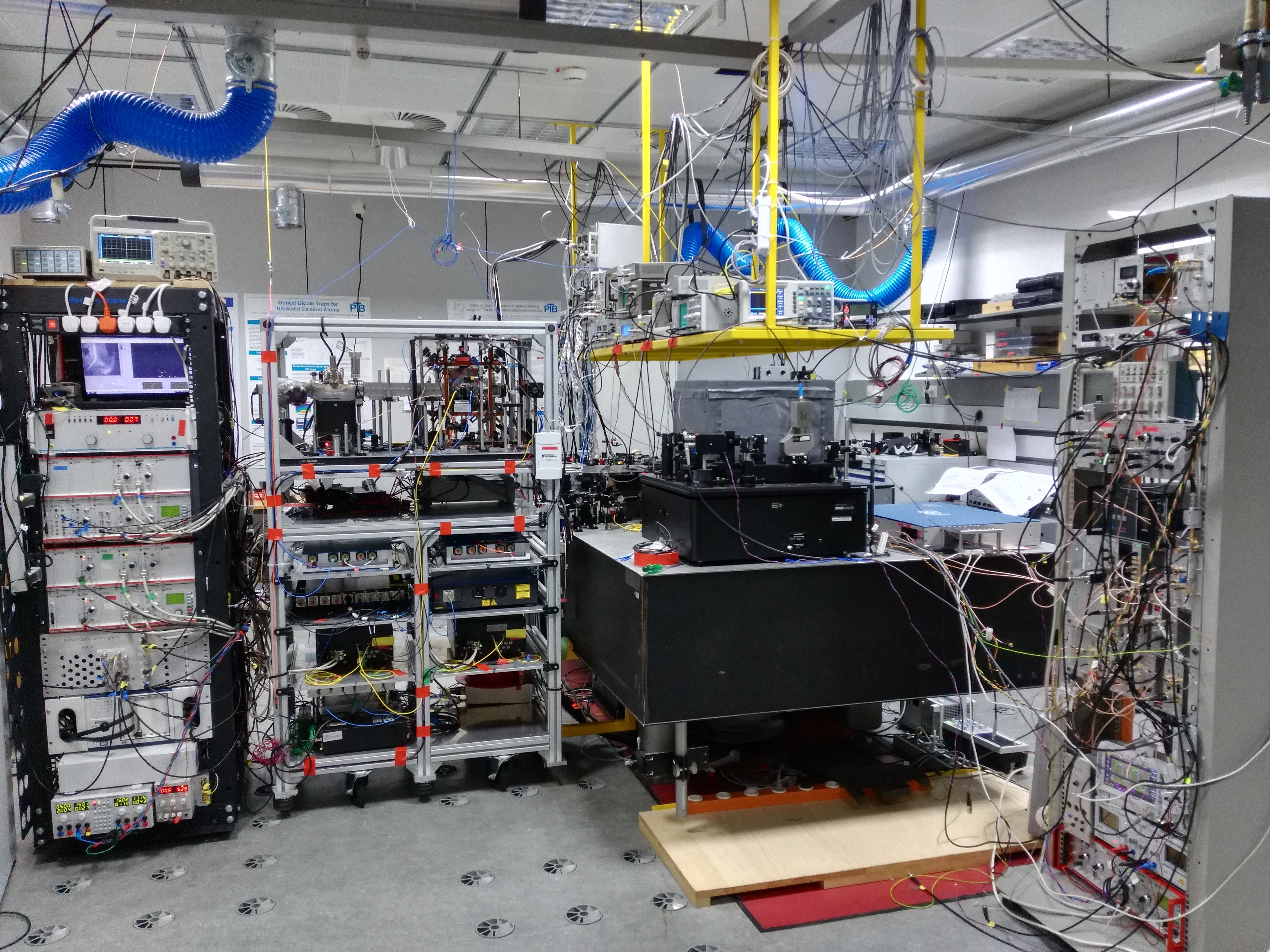
The SOC2 optical clock is an optical strontium-88 lattice clock with a compact modular design for transportability, which is the result of a collaborative efforts between the teams of S. Schiller (Universität Düsseldorf), C. Lisdat (PTB), U. Sterr (PTB) and K. Bongs & Y. Singh (formerly University of Birmingham), funded by the EU and ESA as well as the Universität Düsseldorf.
The SOC2 optical clock was fully characterised in PTB in 2018, taking advantage of PTB's ultra-stable clock laser and comparison with PTB's stationary clock. The performance achieved in 2018 was 2×10-17 uncertainty and 3×10-18 instability at an integration time of 30,000 s.
Publications:
- Test1
- Test2